Editor’s Note: Indeed’s AI at Work is a series of insightful research reports from Hiring Lab, Indeed’s economic research arm. This research is designed to provide data and new insights into the impact of AI on the labor market to help employers and job seekers better understand and prepare for the changing workforce. For an in-depth examination of the international rise of broad artificial intelligence jobs and more-specific generative artificial intelligence roles, please find our additional research here.
Key Points:
Virtually every job will face some level of exposure to potential GenAI-driven change. But while GenAI can learn to do some tasks reasonably well, it is unlikely to fully replace many jobs— especially those that require manual skills and/or deep personal connections. For a PDF summary of key findings from this research, please click here. And for a PDF version of the entire report, please click here.
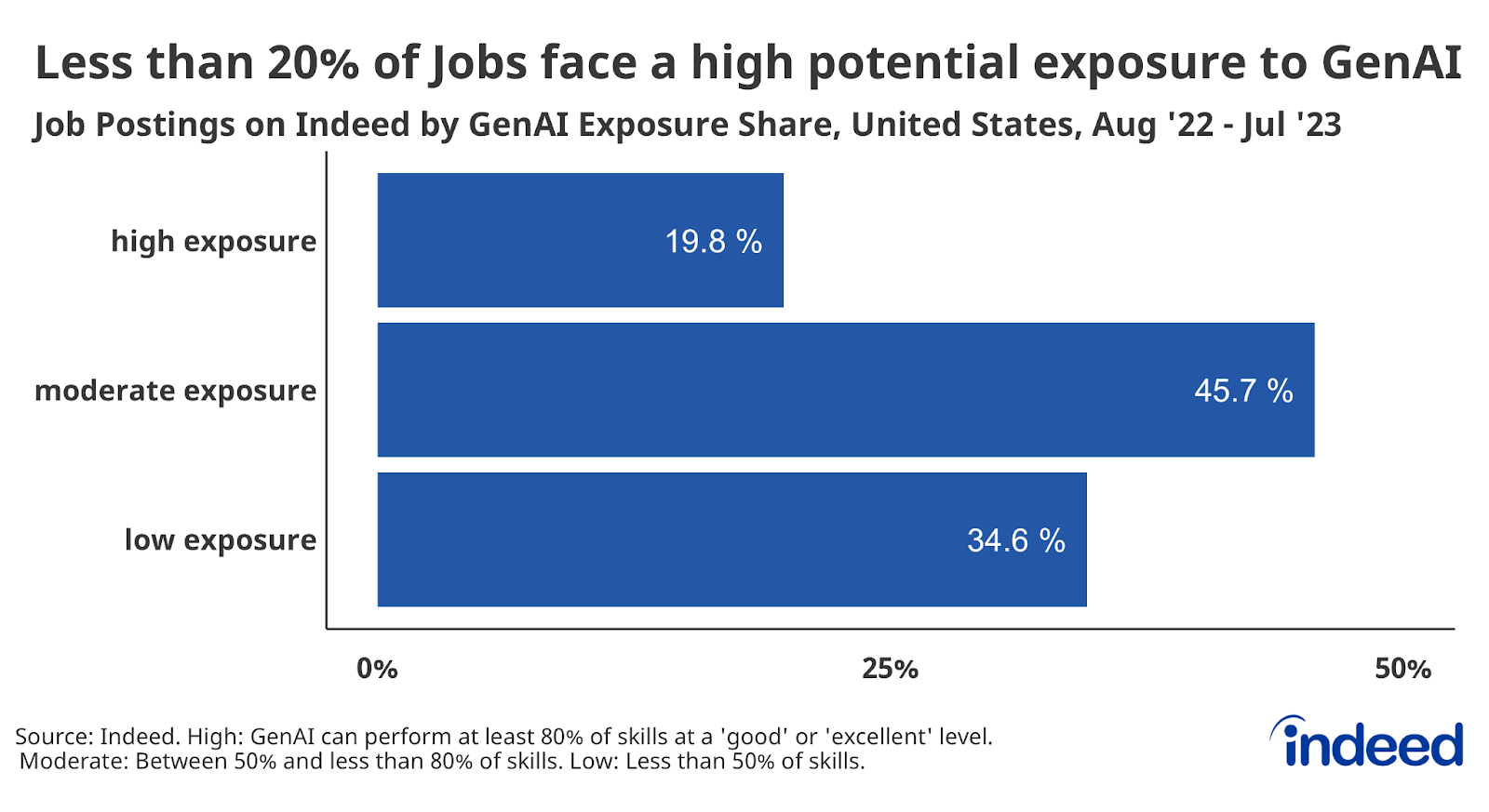
- All jobs face some potential exposure to GenAI-driven change. While only 19.8% of jobs face the highest level of potential exposure, more than a third (34.6%) face the lowest potential exposure.
- Unlike prior advances in robotics and computing that largely impacted manual labor, roles filled by knowledge workers are potentially the most exposed to change from generative AI.
- Driving roles face the lowest potential exposure to skills GenAI could reasonably replace or augment, while software development roles face the highest potential exposure.
- As the labor market continues to adjust to the rise of remote work, the higher the odds are that a job can be done remotely, the greater its potential exposure is to GenAI.
- Many of the jobs most in demand from employers in today’s tight labor market are among those with the least potential exposure to GenAI-driven change. A majority (20) of the 25 most common jobs posted on Indeed currently face a lower potential exposure to GenAI than the average job posting.
Every job is potentially exposed to some kind of change from generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) technology—ranging from a comparatively low potential exposure in driving jobs, to a high potential exposure for many tech jobs. But GenAI is unlikely to fully replace many jobs. Instead, as the technology continues to learn certain skills associated with certain jobs, it will augment or transform some more than others. Ultimately, GenAI is more likely to remain only decent (at best) at performing most tasks, rather than truly masterful, and is currently bad at more skills than it is good at.
But don’t just take our word for it. When asked, GenAI reached the same conclusions about itself.
Starting with a universe of more than 55 million job postings mentioning at least one work skill published on Indeed over the past year, we identified more than 2,600 individual skills within those jobs and organized them into 48 skill families. We then asked ChatGPT, a leading GenAI tool, to rate its ability—either poor, fair, good, or excellent—to perform each skill family, with all skills within a given family assigned the same rating as the family overall. Within all occupational groups analyzed, there are at least some skill families that GenAI says it can perform excellently.
But that does not mean it can perform entire jobs excellently—far from it, in fact. GenAI said it was “excellent” at only four of those 48 skill families, and “good” at another 16. It rated itself as poor or only fair at performing a majority (28) of the 48 total skill families analyzed. And even where GenAI does have a strong ability to do a given job, it is hardly a true expert: GenAI said it was good or excellent at 80% or more of all skills in less than a fifth (19.8%) of all job postings analyzed.
Those one in five jobs in which 80% or more skills can be done “good” or “excellent” by GenAI were determined to have the highest potential exposure to GenAI-driven change. Jobs in which between 50% and less than 80% of skills can be performed good or excellent were determined to have a moderate potential exposure to GenAI. Jobs in which less than half of skills could be done good or excellent were determined to have a low potential for exposure.
This research shows that the human element required in many critical job skills—including empathy, intuition, and manual dexterity—remains irreplaceable. GenAI, while adept at processing data and executing specific tasks, lacks the innate human qualities that define various roles, especially those centered around manual work, human interactions, and decision-making based on nuanced understanding. A GenAI chef can help refine a recipe or translate a menu, but it can’t chop an onion or garnish a dessert. A GenAI nurse can help diagnose an illness, but can’t insert an IV or console a worried family. A GenAI software developer can write a line of code, but can’t place it within the broader, complex software architecture envisioned by a human developer. There are certain work skills unique to humans that simply can’t be automated.
Where there’s a skill, there’s a way
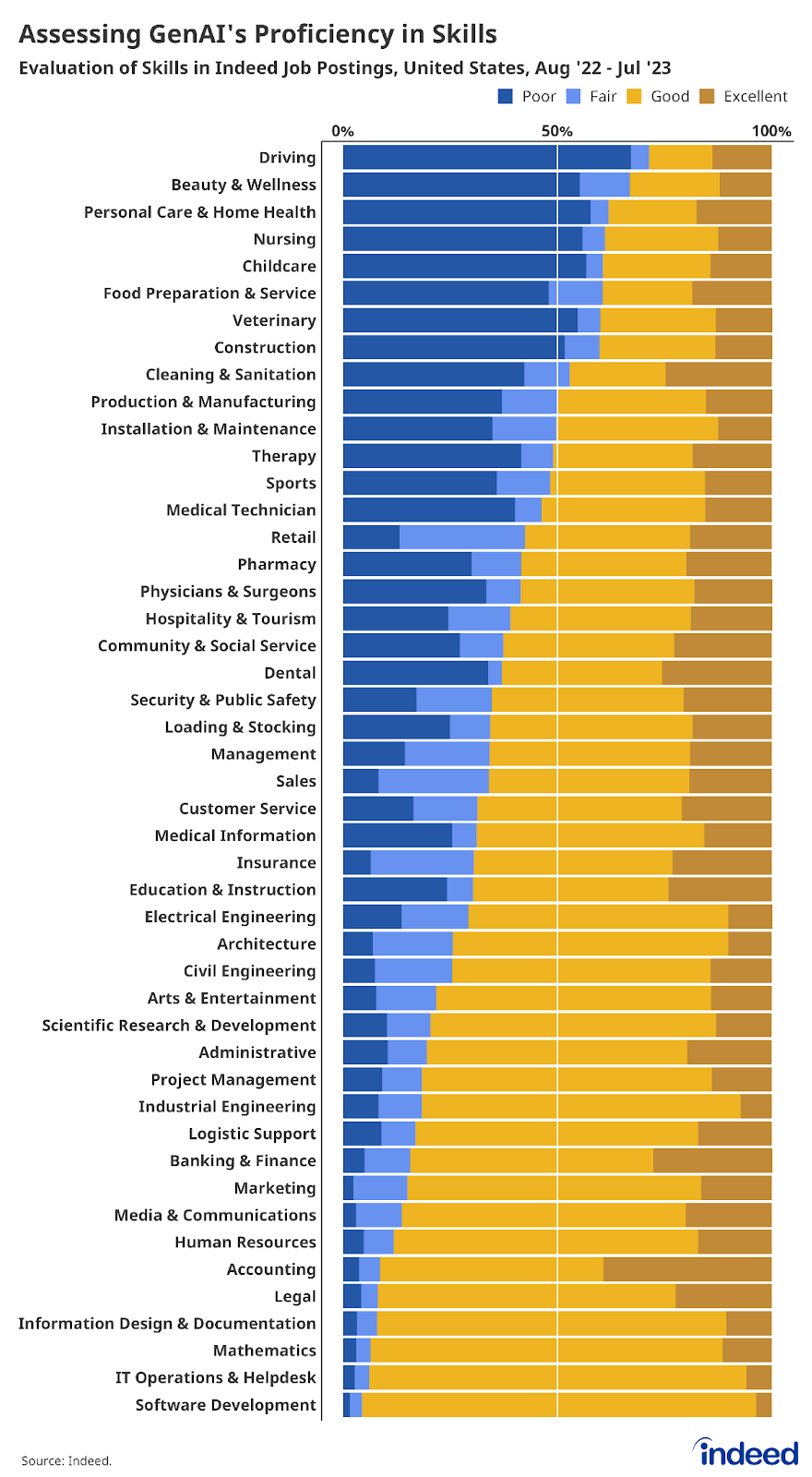
Every job is characterized by a mix of individual skills required to do that job, and it is these individual skills that GenAI is learning to perform. However, the exact number of skills mentioned in a given job posting varies a lot across occupations. The average job posting on Indeed over the past year mentioned four skills. Job postings for dental, personal care & home health, driving, cleaning & sanitation, and beauty & wellness roles mentioned the fewest individual skills on average (2). Job postings for tech/software roles mentioned the most on average (12). From these skills, Hiring Lab created 48 thematic skill families ranging from animal care & handling skills to visual & performing arts skills.
Technology skills in particular—ranging from the very broad, such as “computer skills,” to the very specific, such as “java”—are incredibly important when considering the future of work and the potential for disruption represented by GenAI. These skills are present to some extent across every occupation category analyzed by Indeed (though not necessarily within every posting under that category), and they are among the skills that Generative AI is most poised to transform. On average, roughly one in five (18.4%) skills mentioned in a typical Indeed job posting is a technology skill, and almost 40% of the 2,600+ individual skills identified for this analysis fell under the “technology skills” family, one of the 16 skill families at which GenAI said it was “good.”
Where GenAI is good, bad, & in-between
It is this relative abundance or scarcity of required technology skills—and other skill families that GenAI says it is good (or bad) at performing—that largely helps define the listing of occupations that are most- and least-exposed to potential GenAI-driven change. Broadly, while GenAI is relatively good at technical skills (and jobs), it is pretty bad at skills (and jobs) that require intuition, reasoning, and/or in-person, manual work.
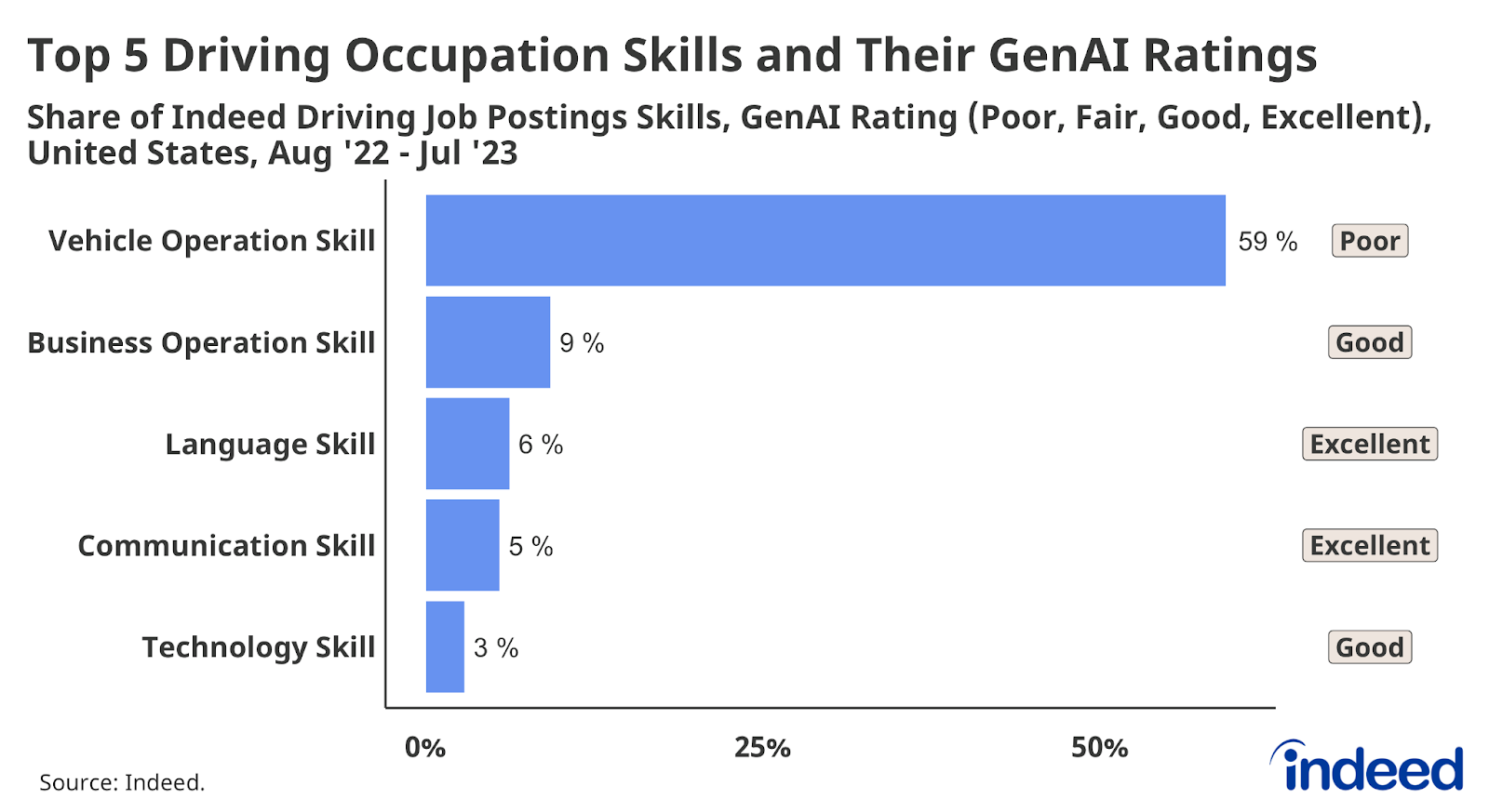
Among all occupation groups analyzed by Indeed, driving jobs had the lowest potential exposure to skills that GenAI says it can do at least reasonably well. GenAI said it was “good” or “excellent” at only 29% of all skills specified in driving job postings. Almost 60% of all skills mentioned in a typical driving occupation job posting are in the “vehicle operation” skill family—a family in which GenAI rated its own ability to perform those skills as “poor.” Business operations skills—which GenAI rates itself “good” at—represent 9% of skills in a typical driving post, and are mentioned in just 28% of driving job postings. Communication skills and language skills, among the four skill groups that GenAI says it is “excellent” at (along with math skills and finance skills), appear in only 18% and 10% of driving job postings, respectively.
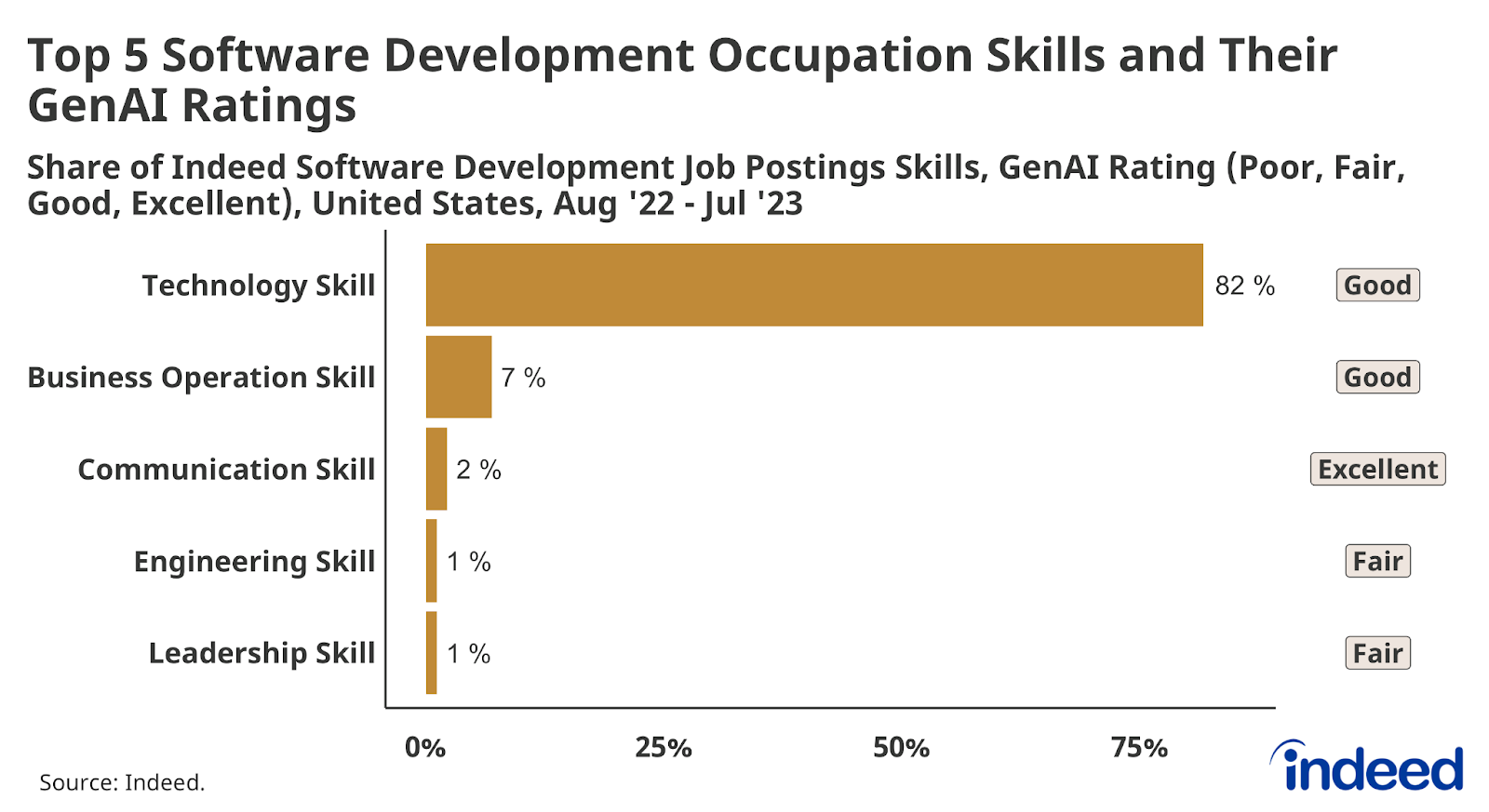
At the other end of the ranking, software development occupations had the highest potential exposure to skills GenAI said it can do at least reasonably well—GenAI said it was “good” or “excellent” at more than 95% of all skills specified in software development postings. Technology skills represent 82% of skills noted in a typical software development post. Business operations skills—which GenAI rates itself “good” at—represent just 7% of skills in a typical software developer posting, but are mentioned in 71% of all software development job postings. Communication skills—which GenAI rates itself “excellent” at—are mentioned in almost half (43%) of all software development job postings. GenAI says it is only “fair” at engineering skills and leadership skills, which are found in 20% and 12%, respectively, of all software development job postings—but with each representing just 1% of skills noted in a typical posting.
These two extremes may be somewhat obvious in terms of potential exposure to GenAI. For drivers, a large language model of the type that powers many generative AI tools might be able to plan a route on a map, but GenAI will never be able to turn a steering wheel (though other artificial intelligence technologies will). For software developers, however, those models are likely to be much better at writing an efficient line of code or preparing/summarizing technical documentation.
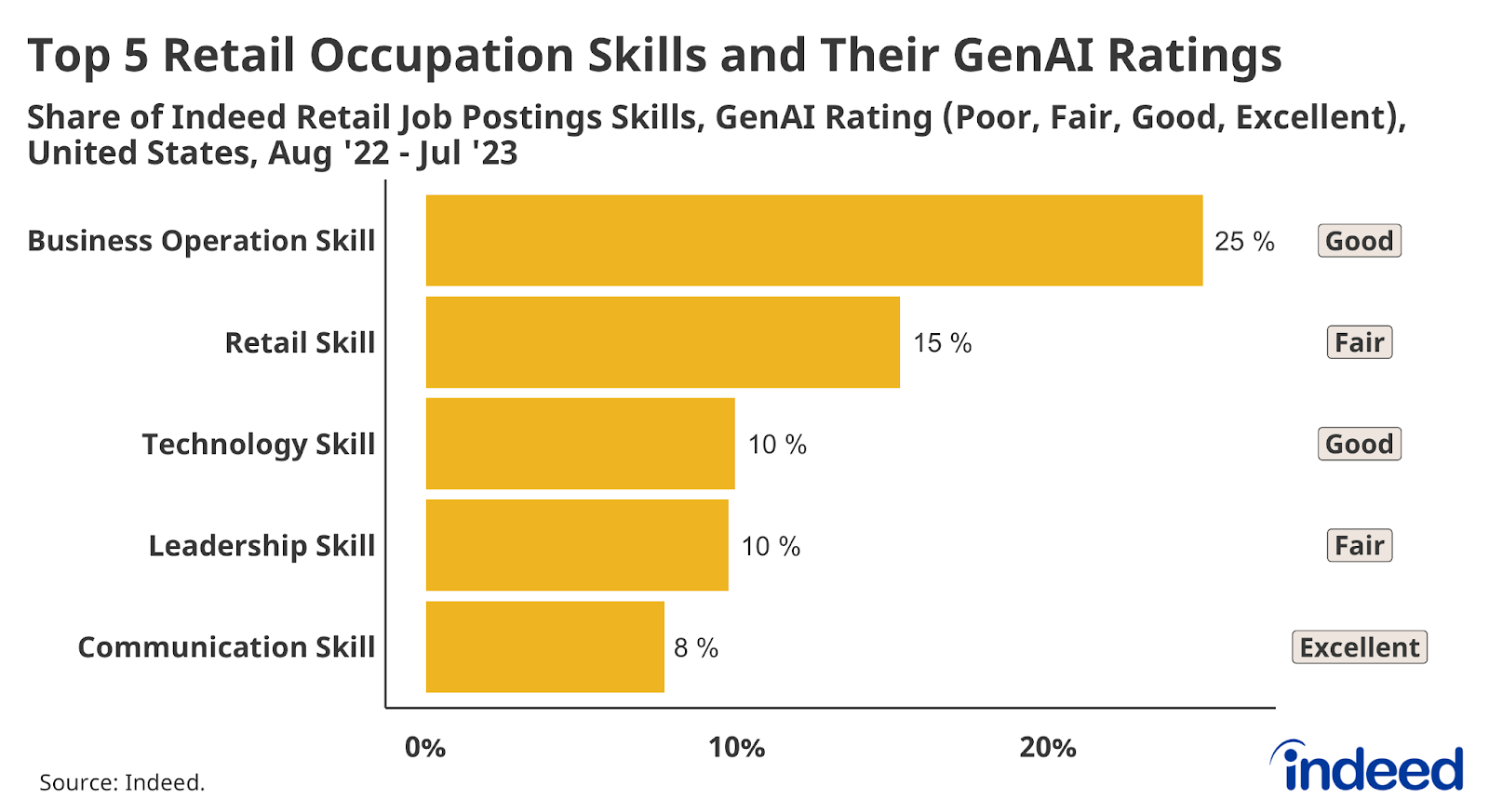
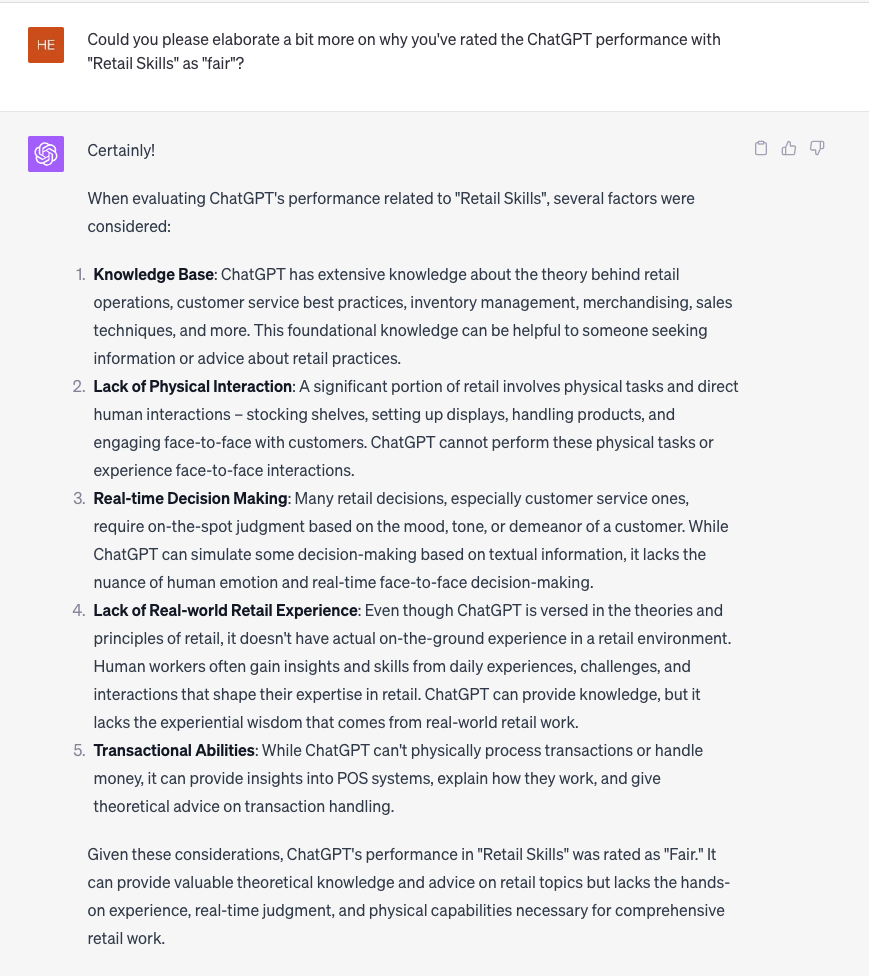
It’s the jobs that fall somewhere in the middle—including retail—that are arguably the most interesting cases to study when trying to determine the potential impact of GenAI on the future of work. GenAI said it was “good” or “excellent” at a small majority (57.6%) of all skills specified in retail job postings. Business operations skills—a family that GenAI says it is “good” at—represent 25% of the skills in a typical retail job posting, and are mentioned in 77% of retail job postings. But after business skills, the core of retail jobs are retail skills, which are found in 65% of retail job postings and represent 15% of the skills found in a typical retail posting. GenAI rates itself as only “fair” at retail skills, and it is worth examining its own full explanation for its so-so rating. Essentially, GenAI says it can help with retail strategy, but cannot perform the person-person skills necessary for retail success.
Here is what the tool had to say about its own ability to perform retail skills:
Remote jobs are more exposed, common jobs are less exposed
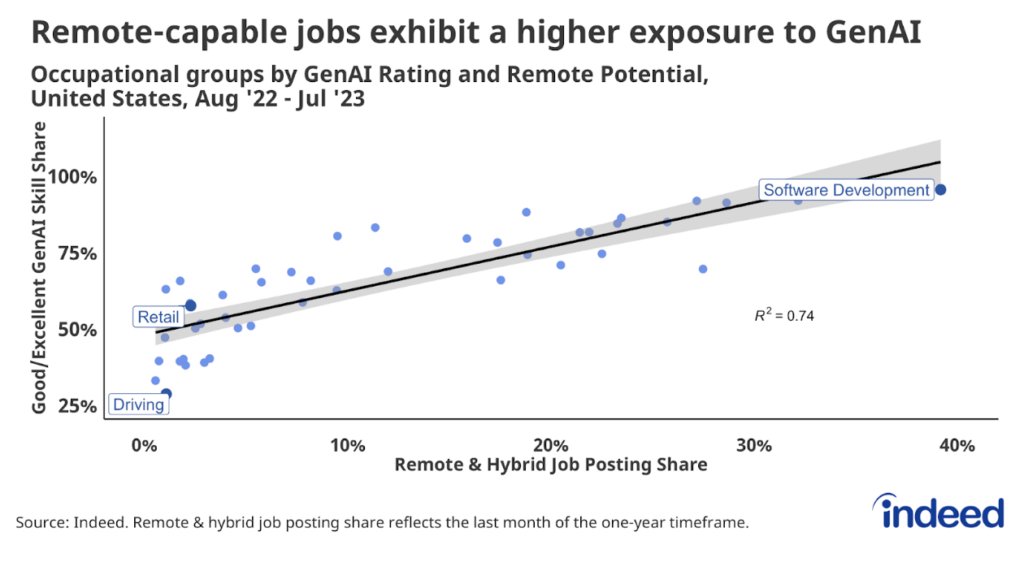
Additionally, we combined the skills data from this research with Hiring Lab’s Remote & Hybrid tracker, which analyzes the share of job postings advertising remote work opportunities across occupations. We found that jobs with the least potential exposure to GenAI (including driving, cleaning & sanitation, and beauty & wellness) are also those with the lowest ability to be done remotely. The higher the odds are that a job can be done remotely, the greater its potential exposure is to GenAI-driven change. Historically, these are not the kinds of jobs that have been subject to disruption through automation, more evidence that this round of technological evolution will affect different workers in different ways than in the past.
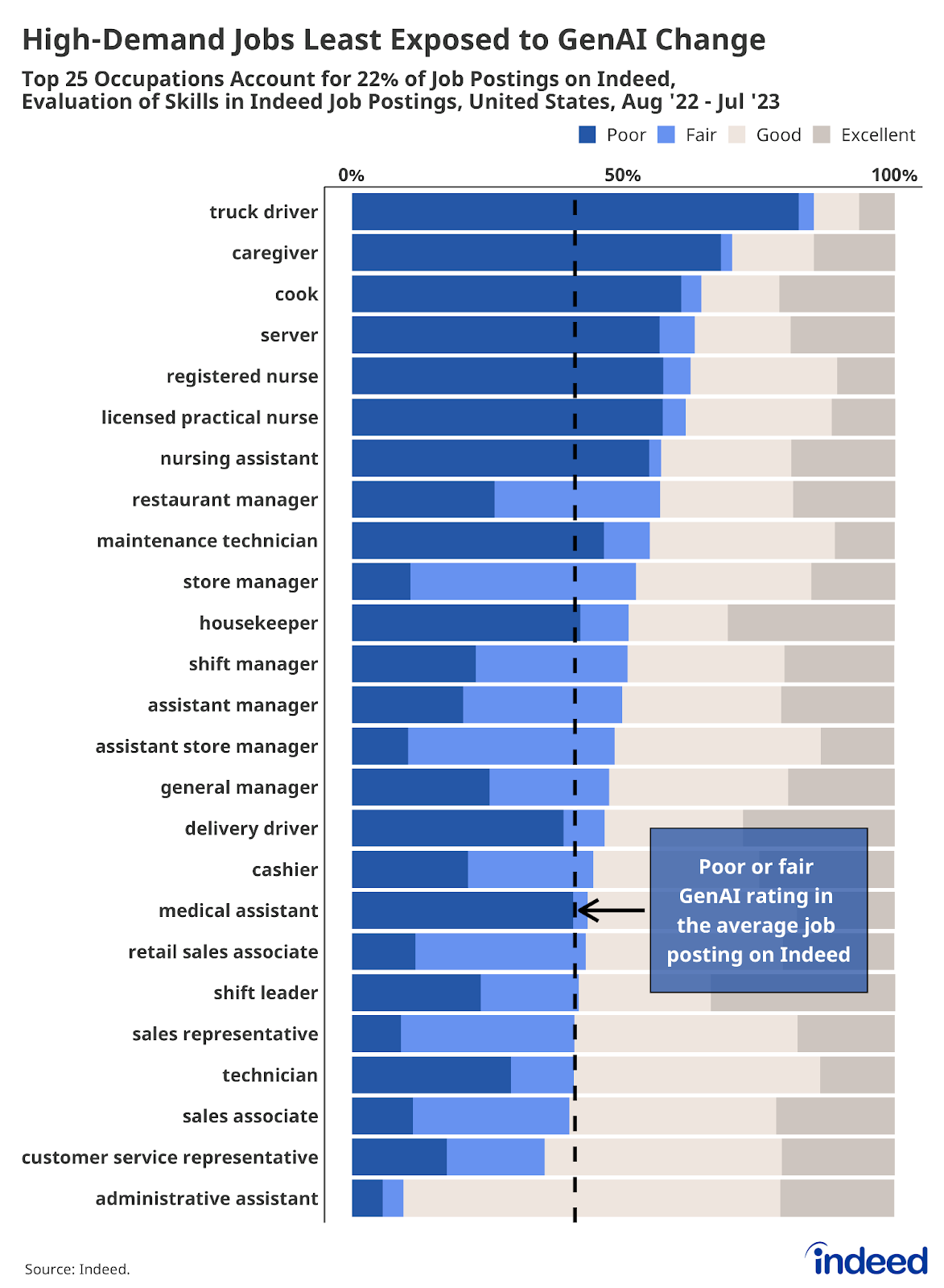
Finally, while all jobs do face some potential exposure to GenAI-driven change, the jobs most currently in demand by employers are among the least exposed. A majority (20) of the 25 most common jobs posted on Indeed—accounting for 22% of all Indeed job postings—currently face a lower potential exposure to GenAI than the average job posting. GenAI rated itself as poor or fair at 41% of skills mentioned in the average job posting. But in these 20 roles, GenAI rates itself as only poor or fair at more than 41% of skills associated with those jobs. Because the jobs most in demand right now are comparatively less exposed to GenAI-driven change, it’s unlikely that today’s tight labor market will be quickly alleviated by evolving AI technology.
Of these 25 common jobs, truck driver roles currently face the least potential exposure to GenAI (GenAI rates itself “good” or “excellent” at just 15% of truck driver skills). Of these 25 common jobs, administrative assistant roles currently face the most potential exposure to GenAI (GenAI rates itself “good” or “excellent” at roughly 90% of administrative assistant skills).
Conclusion
The findings around the fields most- and least-exposed to potential GenAI-driven change clearly illustrate the different challenges posed by GenAI relative to earlier industrial and commercial automation efforts. Many of the jobs most in demand from employers in today’s tight labor market are among those with the least potential exposure to GenAI-driven change. Unlike earlier advances in robotics and computing that largely impacted and replaced manual labor, it is knowledge workers who are more likely to be impacted by this evolution in GenAI technology. As the labor market continues to adjust to the rise of remote work, the higher the odds are that a job can be done remotely, the greater its potential exposure is to GenAI.
How people work will inevitably change as GenAI gains wider adoption, with GenAI tools augmenting or replacing certain tasks and forcing a rethink of some traditional work profiles. The most automatable tasks—debugging code, documenting work, and identifying relevant data for a diagnosis—will be replaced/supported by GenAI. But as we’ve seen, at its best GenAI is generally good but not great at certain tasks, and at its worst is simply bad. As such, it’s likely that deep, diverse, expert, and uniquely human knowledge will stay in high demand. A person’s capacity for on-the-job adaptation and lifelong learning, already critical today, will only become more important tomorrow.
Methodology
This research focused on job skills mentioned in over 55 million Indeed job postings published in the United States between August 2022 and July 2023. Remote & hybrid job posting share reflects data as of the last month of the one-year timeframe. Indeed identified more than 2,600 individual skills within those jobs and categorized them into 48 families. Then we asked ChatGPT-4.0, a leading GenAI tool, to rate its ability in these families, ranging from poor, fair, and good, to excellent, with each skill within a given skill family assigned the same rating as the family overall. GenAI’s impact was summarized into three exposure levels: low, moderate, and high, providing insights into its proficiency across various skills in the job market.
Jobs in which 80% or more skills can be done “good” or “excellent” by GenAI were determined to have the highest potential exposure to GenAI-driven change. Jobs in which between 50% and less than 80% of skills can be performed good or excellent were determined to have a moderate potential exposure to GenAI. Jobs in which less than half of skills could be done good or excellent were determined to have a low potential for exposure.
This analysis is focused on identified skills only, and does not include data on required/desired licenses, certifications, or academic degrees. We conducted robustness checks using data from rejected candidates on the Indeed platform to evaluate the skills mentioned in job postings. Even when focusing on essential skills that employers require, the results did not reveal significant differences.
Many iterations of the conversation prompt with ChatGPT were used to properly calibrate expectations and realistic skill assessments. Researchers conducted approximately 20 “interviews” with ChatGPT to create the final prompt. For a more detailed explanation of our approach, data used and findings, please see our full methodology post here.



