This post first appeared in Quartz.
The world is in the middle of an economic crisis and it’s impossible to predict what will happen next. Economists’ models are based on a combination of past relationships between economic variables and plausible theories about how forces interrelate. They help explain how inputs like a change in oil prices, or a tax hike, affect outputs like unemployment or GDP.
But pandemics are so rare and unpredictable that economists’ models are less useful. With COVID19, there is still uncertainty on all fronts: How will the virus behave? Will the health system hold up? Will there be a vaccine and, if so, when? How will governments, businesses, and consumers respond? We still don’t know the inputs, so we can’t predict the output.
Under huge uncertainty, we need more imagination and less prediction. Imagining the range of possible scenarios lets us begin to plan. Striving for more accurate predictions might give us a false sense of certainty and blind us to what’s coming.
The acute phase and the chronic phase
We’re in the acute phase of this crisis. The pandemic — and necessary containment efforts — have nearly shut down large sectors of the economy: restaurants, hotels, travel, and much of retail. Some companies that support the stay-at-home economy are rapidly hiring, especially in grocery and online retail, but the hiring numbers are small relative to furloughs and layoffs in other sectors.
This acute phase should come to an end when the pandemic is under control. But if some businesses don’t reopen, if surviving businesses don’t start hiring, and if households can’t spend then we could enter a chronic phase — a recession or depression. We could see a partial rebound in the shutdown sectors even as overall unemployment continues to rise.
No one knows how likely, severe, or long a chronic phase might be. It depends on how long the acute phase lasts and what governments do to support people and businesses. Most optimistically, we could avoid the chronic phase altogether and bounce back strongly after the acute phase ends. More pessimistically, the acute phase could cause chronic damage and a slow, painful recovery.
What it means for job searchers
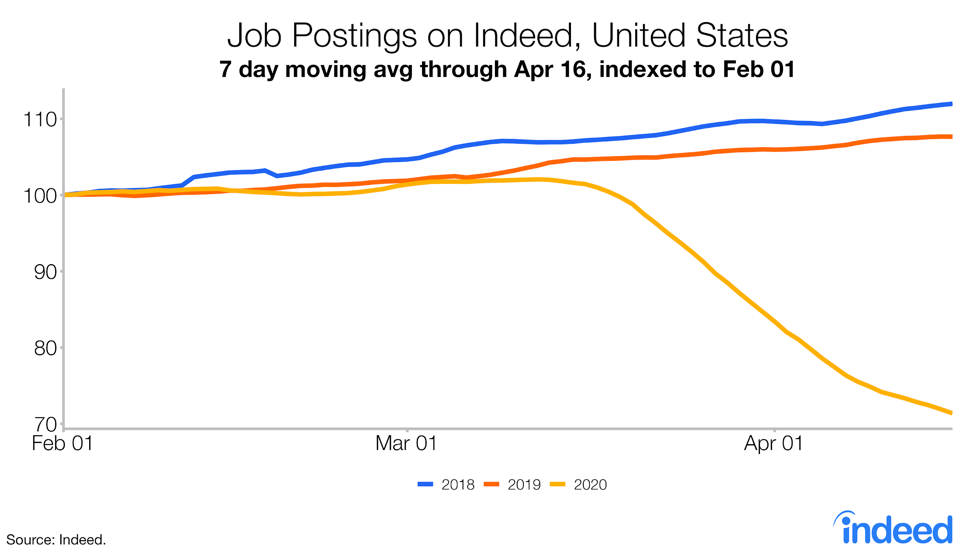
For job seekers, there’s no sugar-coating: It’s a hard time to be looking and could stay that way for a while. As of April 16, job postings are down by a third in the US.
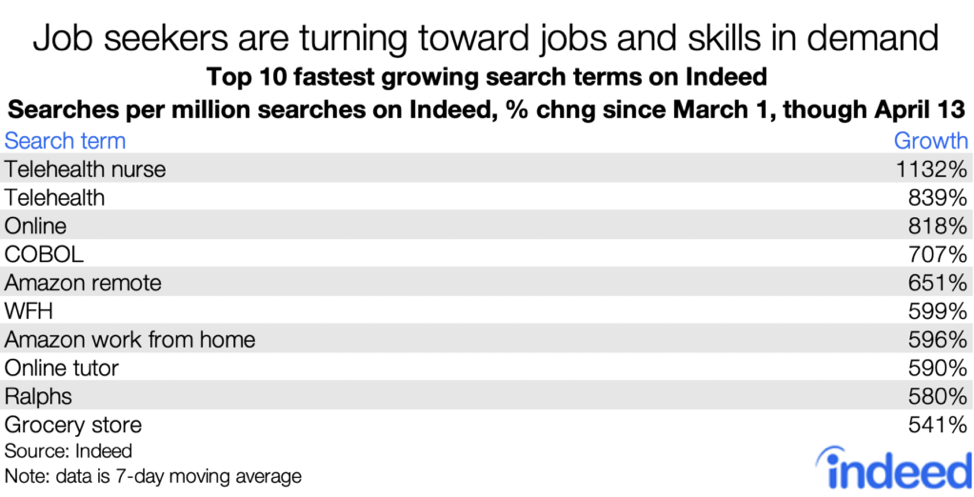
Some people will be less inclined to search — if you’ve got a good, secure job you’ll probably stay put if you can. Few people want to switch jobs and be the last one hired at a new company when uncertainty is high. Remember that the voluntary-quitting rate fell by almost half during last decade’s recession. But many who have lost jobs will be searching, perhaps desperately — especially if having health insurance depends on getting a job, as is typically the case in the US. Job seekers are looking for remote work and for jobs at companies that have announced big hiring pushes.
What it means for hiring
For employers in most sectors, hiring has slowed or is on hold. In sectors that have largely shut down, hiring might rebound once the acute phase of the pandemic is over — though probably not back to pre-COVID19 levels. Some companies whose business support the stay-at-home economy — like grocery stores, online retail & delivery, and pharmacies — are hiring rapidly. But these jobs that support the stay-at-home economy aren’t the work-from-home jobs that many people are seeking.
If we enter a chronic phase, it might look more like a conventional slowdown or recession. It’s highly unlikely we’ll get back to the tight labor market of 2019 any time soon. Rather, there will be more unemployed workers competing for fewer job openings. Employers who are hiring might not need the strategies they used when the labor market was tight — like raising wages, searching more broadly, or investing in training.
The hardest hit
It’s hard to fathom the magnitude of this economic crisis. The early numbers of unemployment insurance claims and payroll declines are staggering — they threaten to break our models and our brains (no y-axis is safe). Abstract numbers so big can numb and paralyze us as we’re trying to understand what’s happening.
While the magnitudes are hard to imagine or predict, it’s clearer who will be hardest hit. Both the acute and chronic phases of this crisis are likely to hurt most those with less education, lower wages, and other labor-market disadvantages, therefore widening inequalities.
In the acute phase, job losses will hurt the least well off. The most shut-down sectors tend to be lower-wage jobs. The vast majority of job losses according to the March 2020 jobs report were in lower-wage industries. And households and businesses that were struggling to begin with have the thinnest cushions for surviving the acute phase of this crisis.
Recessions tend to worsen inequalities. In the chronic phase of a prolonged slowdown or recession, the gap between the haves and have-nots will widen — a reversal of the narrowing that the tight labor market brought.
Which data to watch
The definitive, comprehensive measures of the labor market — like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics’ monthly jobs report and JOLTS — are snapshots of the economy from several weeks earlier. When the economy is changing as rapidly as it is now, these reports are outdated by the time they’re published.
A closer-to-real-time view comes from weekly unemployment insurance claims, surveys and sentiment indexes, and job-postings data on Indeed, where I work, as well as industry data like restaurant bookings and airport passenger counts. All are showing dramatic deterioration in the labor market and will be the data to watch for the first signs of a turnaround. These sources are critical for tracking the acute phase of this crisis.
Still, the definitive government reports will catch up. And, even when lagged, they offer essential insights about which sectors and people are most affected.
The future of work and everything else
How we work and live during a pandemic is a poor guide to post-pandemic life. Some of this huge forced experiment of the stay-at-home economy might be a success: some people and their employers will want to continue working from home, while others can’t wait to get back to the office. People will discover which new habits they’ll want to sustain and which routines from pandemic life they’ll never want to have to do again.
It’s way too early to say what the pandemic means, longer-term, for specific industries, jobs, or places. My sense is that the predictions people are making — about the demise of particular industries, or the rise of labor activism, or fleeing cities for the suburbs, or giving up car-dependence — say more about the forecaster’s own hopes or fears than about how the world is likely to change. Coronavirus doesn’t kill cognitive bias.
My own hunches are that more people will work remotely, but the end of the tight labor market will give employers more bargaining power. International travel, trade, and cooperation may all suffer, and people will be spending less and saving more. Or perhaps not. We’re in for a sustained period of uncertainty about what the future normal will look like and how long it will take to get there.